 Companies around the world are committed to environmentally friendly practices when it comes to manufacturing processes. Businesses that produce byproducts in their manufacturing process must figure out a way to properly dispose of them. Companies like chemical manufacturers, food and beverage processors, as well as pharmaceutical corporations create liquids that need to be treated in accordance with local regulations before they can be released into a sewer system. If these byproducts are not dealt with properly, they will pose a risk to the environment.
Companies around the world are committed to environmentally friendly practices when it comes to manufacturing processes. Businesses that produce byproducts in their manufacturing process must figure out a way to properly dispose of them. Companies like chemical manufacturers, food and beverage processors, as well as pharmaceutical corporations create liquids that need to be treated in accordance with local regulations before they can be released into a sewer system. If these byproducts are not dealt with properly, they will pose a risk to the environment.
Companies are also looking for ways to recycle water as a way to reduce costs. To do this, they must invest heavily in the treatment processes used to recycle water.
Industrial pumps are at the heart of wastewater treatment systems, with different pumps being used throughout the treatment process. Positive displacement pumps play a key role in the process.
Positive Displacement Pumps
So, what is a positive displacement pump and what exactly does it do? A positive displacement pump makes fluid move by trapping a fixed amount and forcing (displacing) that trapped volume into the discharge pipe. Pressure is obtained as the liquid is displaced through the pump discharge into the system, thereby converting energy to pressure. The pressure on the pump is a function of the systems reaction to flow.
This type of pump is used in wastewater treatment systems because it can handle a wide range of fluids and solids materials. Positive displacement pumps are generally used in applications involving higher viscosity fluids, like thicker sludges and slurries, thick oils and complex feeds (emulsions), as well as foodstuffs or biological fluids. Positive displacement pumps are recommended for use when accurate dosing or metering is required, like with feeding dewatering equipment where the flow rate is controllable by changing the pump speed.
Types of Positive Displacement Pumps
There are two main types of positive displacement pump technologies: reciprocating pumps and rotary pumps. Each technology has several different designs. Rotary pumps include progressive cavity, rotary lobe, gear, peristaltic, and vane. Reciprocating pumps include piston, plunger, mechanical diaphragm, air actuated diaphragm, double disc and sliding shoe. The main designs used in wastewater sludge handling are progressive cavity, rotary lobe, plunger and double disc. Each of these technologies offers a different set of features and benefits.
Reciprocating Pumps
Reciprocating positive displacement pumps operate by creating a vacuum when a pumping element moves away from the head or seat on the suction cycle. The vacuum draws the liquid into the chamber. The fluid is mechanically trapped between valves and moved out of the chamber on the discharge cycle. Depending on the pump technology, the pumping element is either with a piston, plunger, disc or diaphragm.

A reciprocating pump’s motion is created by the pump’s power source. This can be an electric motor, engine, etc. With the help of a connecting rod and eccentric cam, the reciprocating motion is translated to the pump element in the pump housing. When the eccentric cam moves from the inner center to outer center, a vacuum effect is created in the cylinder. When the piston moves to the outer center to the inner center, the piston forces the liquid to the discharge outlet. Internal ball check valves are typically used to isolate the vacuum and pressure cycles, moving the liquid from suction to discharge.
One unique style of reciprocating pump is the Double Disc Pump. A double disc pump is a double-acting technology based on a non-captive free disc design. The discs in this type of pump act as both the pumping element and valving element to create vacuum and pressure simultaneously to move fluid from suction to discharge. This technology does not use internal ball check valves which are required by other reciprocating pump technologies.
Rotary Pumps
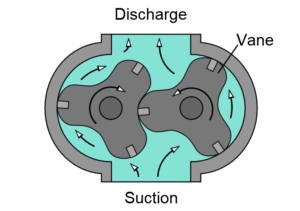
Rotary pump technologies have a fixed stator or casing containing rotating pumping elements actuated by rotation of a driveshaft. The pumping elements in a rotary pump are characterized by close tolerances or a rubbing action to generate flow. These close tolerances eliminate the need for internal check valves. The pump elements are typically referred to as rotors, lobes, gears, screws, or similar elements that are actuated by rotation of the drive shaft.
There are a number of different rotary pumps, including rotary lobe pumps that use internal lobes to create fluid displacement, gear pumps that use the meshing of gears to pump fluid by displacement, screw or progressive cavity pumps that move fluids or solids along the screw axis as a single screw rotates in a cylindrical cavity, moving the material along the screw’s spindle, and rotary vane pumps that have vanes mounted to a rotor that rotates inside a cavity.
Ideal Applications for Positive Displacement Pump Use
Positive displacement pumps are often used to pump high viscosity fluids, like oil, paint, resin or foodstuffs. They are favored over centrifugal pumps in any application where accurate dosing or higher viscosity/higher percent solids material needs to be handled. The output of a positive displacement pump is marginally affected by changes in pressure.
There are a variety of positive displacement pumps on the market, including:
- Double disc pumps used in municipal, industrial, chemical and food processing applications
- Piston pumps used for high pressure washing and other low viscosity liquids, oil production as well as paint spraying
- Plunger pumps used in industrial applications and chemical manufacturing
- Diaphragm pumps used for metering or dispensing, spraying and cleaning, water treatment, paints, oils and corrosive liquids
- Gear pumps used for pumping high viscosity fluids in petrochemical, chemical and food industries
- Lobe pumps used in chemical and food industries, as well as sanitary, pharmaceutical and biotechnology
- Progressive Cavity pumps used in oil production, fuel transfer and irrigation
- Vane pumps use for low viscosity fluids, automotive transmission systems, fuel loading and transmission and drink dispensers
A positive displacement pump is an excellent choice when viscous liquids need to be moved without loss of flow and efficiency. These types of pumps do this by repeatedly enclosing a fixed volume, with the aid of seals or valves, and moving it mechanically through the system.
Learn more about how the reciprocating style Double Disc Pump compares to rotary pumps or diaphragm pumps, as well as other applications of the Double Disc Pump.